Pathogenesis Of Alzheimer's Disease
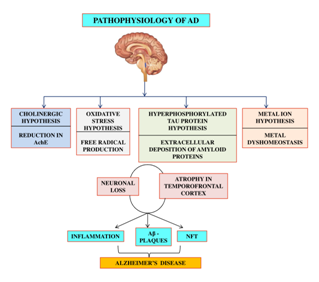
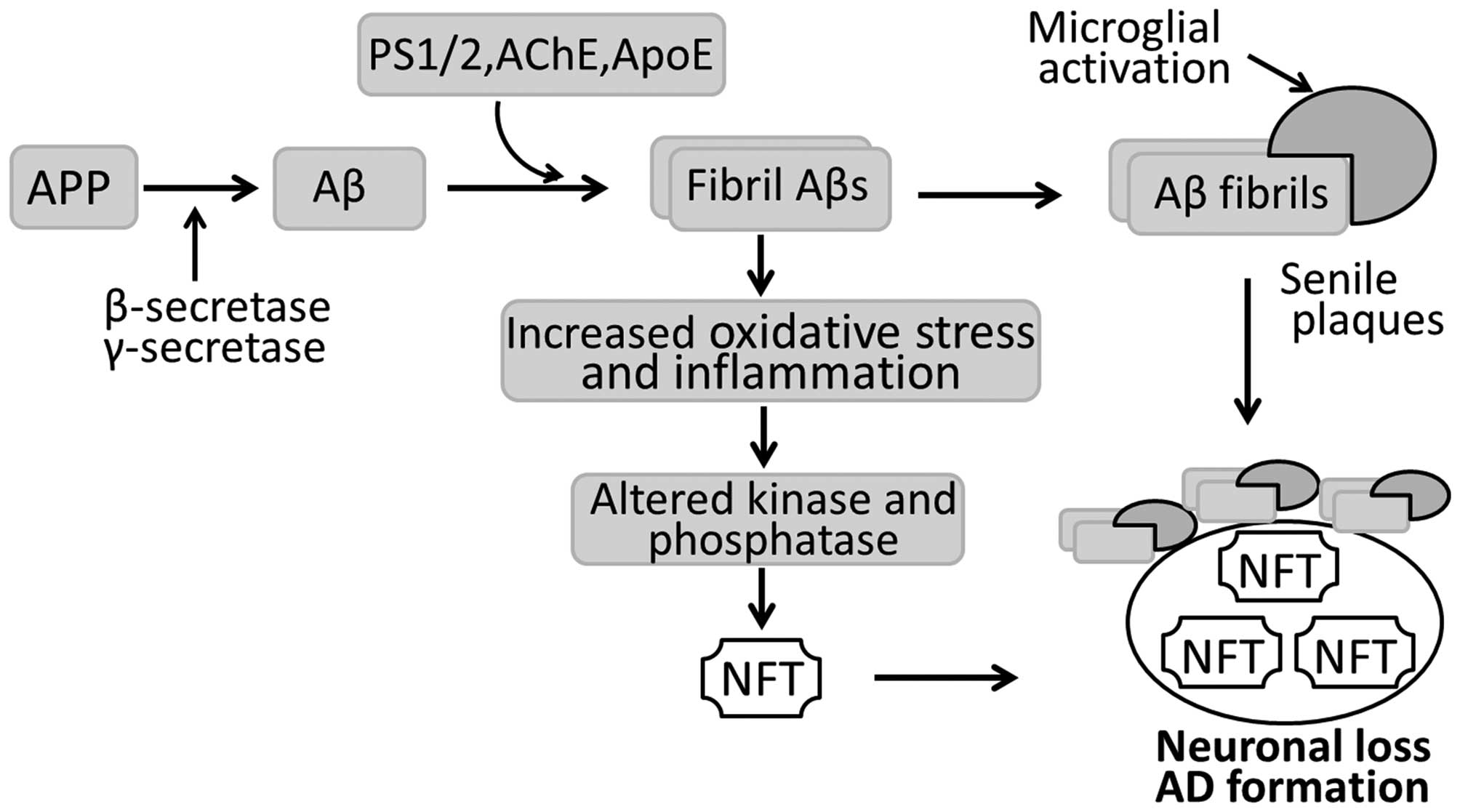
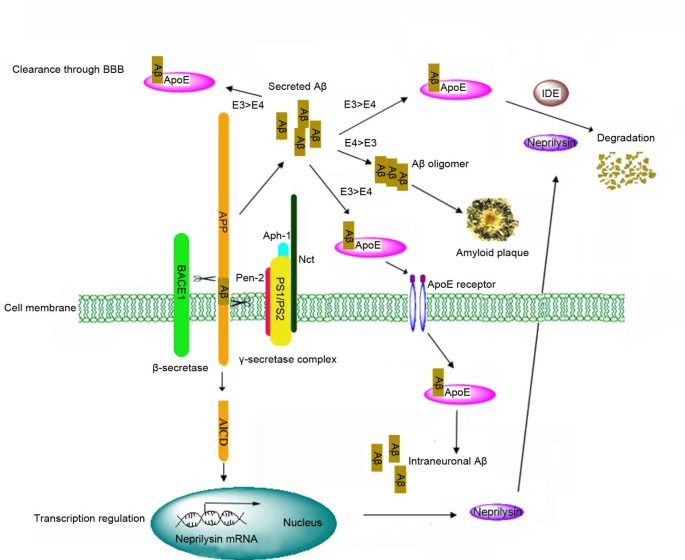
Pathogenesis of alzheimer's disease. Ongoing efforts to understand AD. A the Aβ-amyloid hypothesis b the Aβ-amyloid oligomer hypothesis c the presenilin hypothesis d the Ca2dysregulation hypothesis e the lysosome hypothesis and f the tau hypothesis Fig. Alzheimers disease pathogenesis Table 1 Genes implicated in familial autosomal dominant AD Gene Chromosome Proportion of AD Amyloid precursor protein 21 25 known families.
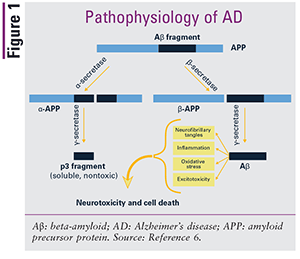
Clinically it is characterized by loss of memory inability to learn new things loss of language function a deranged perception of space inability to do calculations indifference depression delusions and other manifestations. Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia. In addition to deposits of amyloid β Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles growing evidence demonstrates that complex and multifaceted biological processes can arise during Alzheimer disease AD pathogenesis.
PATHOGENESIS OF ALZHEIMERS DISEASE. Several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers disease AD possess significant vascular pathophysiology such as the disruption of BBB integrity and function Kapasi and Schneider 2016 Sagare et al 2012 Yarchoan et al 2012 Zlokovic 2011. Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia.
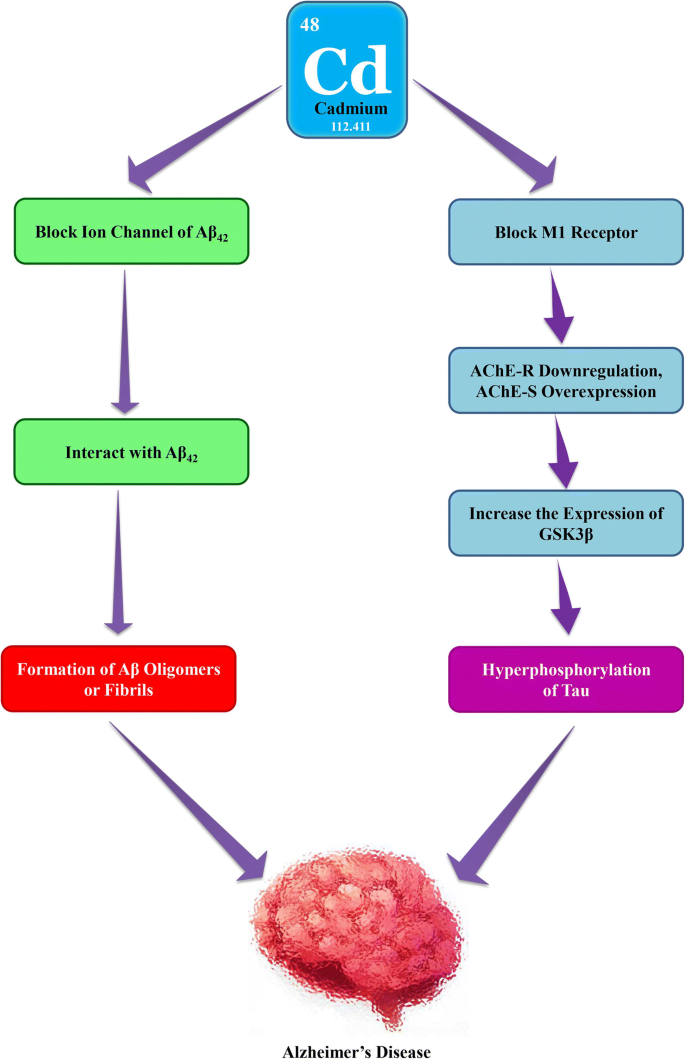
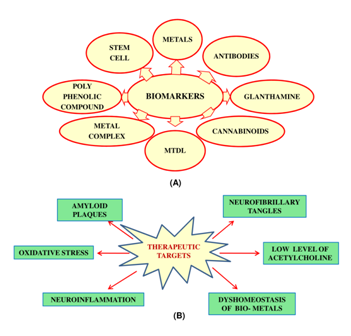
A number of hypotheses have been proposed that may explain AD pathogenesis. Kelch-like ECH associated-protein 1 Keap1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 Nrf2 signaling pathway is thought to be the key regulatory process defensing oxidative stress in multiple organs. Alzheimers disease AD is incredibly common.
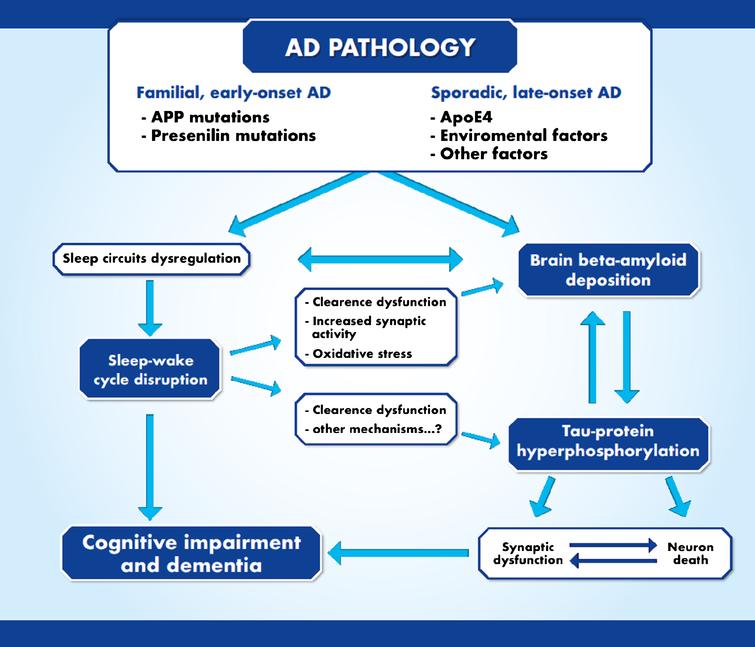
Late-onset AD is genetically and etiologically heterogeneous in nature with innumerable genes and environmental factors involved in disease progression rate and risk. It manifests as a decline in short-term memory and cognition that impairs daily behavior. A growing number of literatures have suggested a possible link.
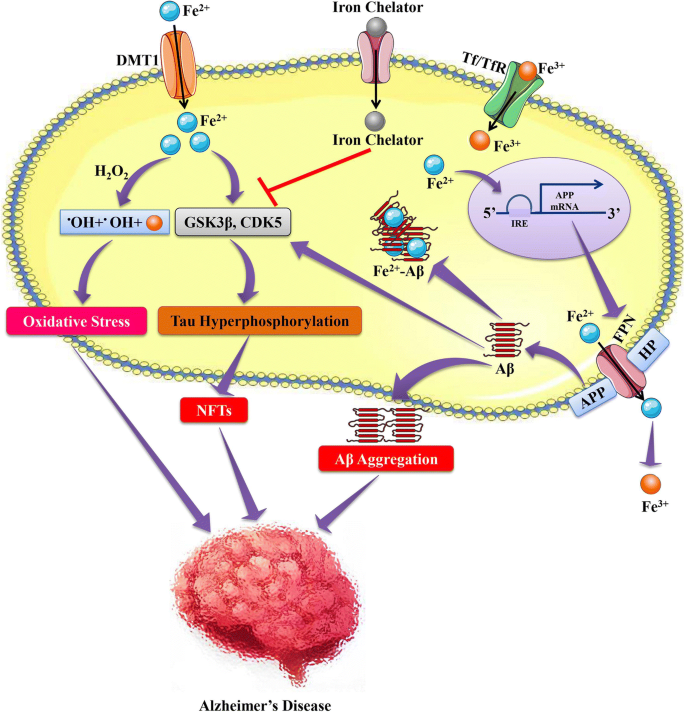
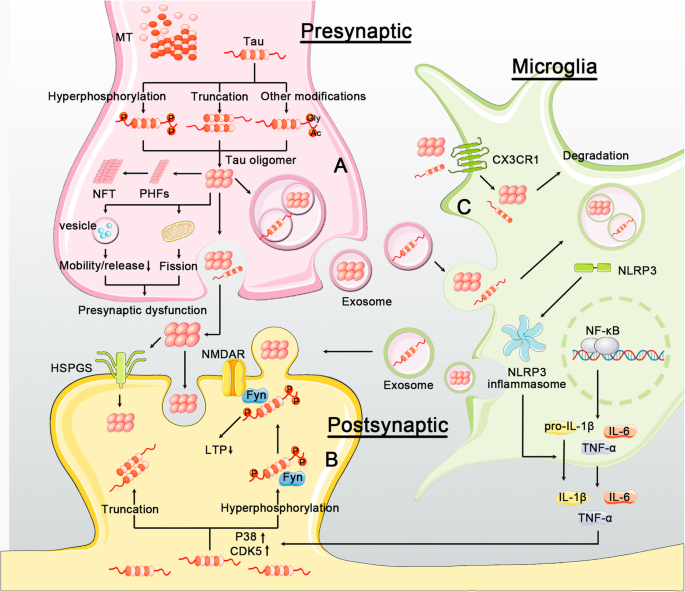
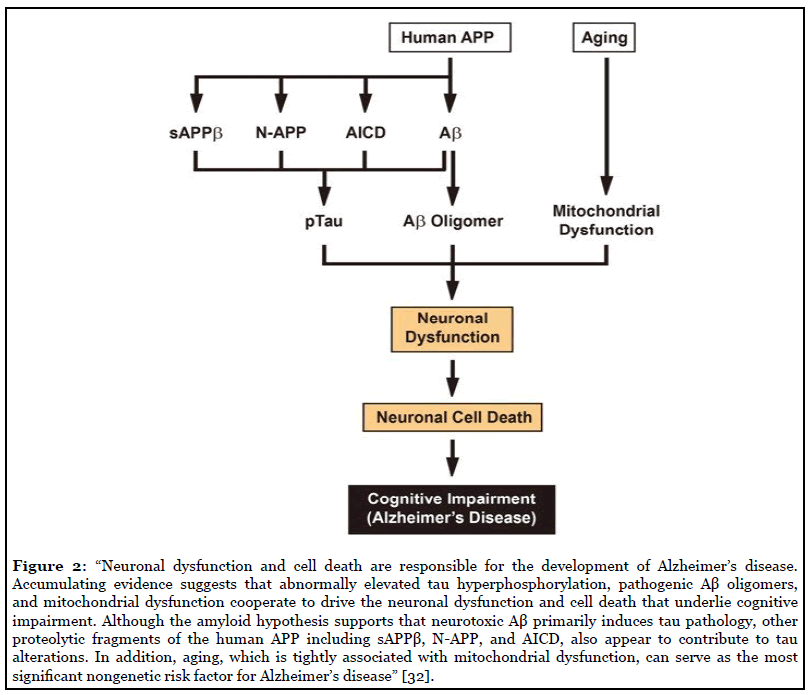
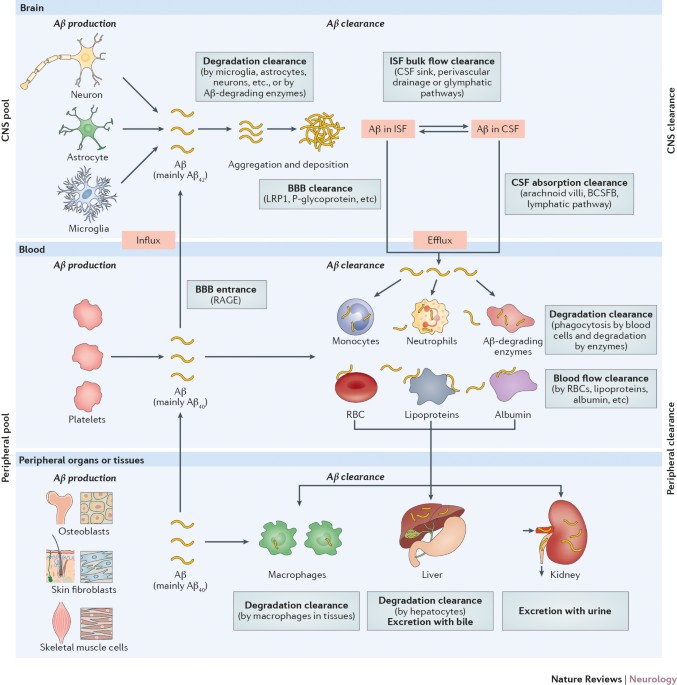
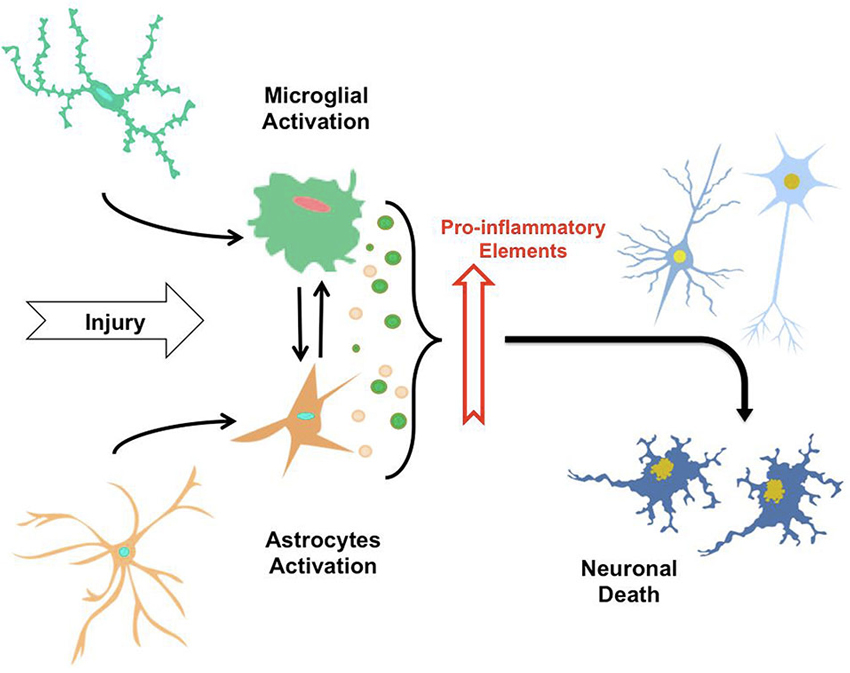
AD is a neurodegenerative disease and its pathogenesis has been attributed to extracellular aggregates of amyloid β Aβ plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles made of hyperphosphorylated τ-protein in cortical and limbic areas of the human brain. While amyloid-β Aβ deposition and neurofibrillary tangle formation in the brain are central pathological hallmarks in AD cerebrovascular lesions and BBB alteration have also been shown to frequently coexist. Impaired gut microbiome flora inhibits the autophagy-mediated protein clearance process.
Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia. In the light of current literature we describe three different linkages between the present gut microbiome hypothesis and the other major theories for the pathogenesis of AD as follows.
Etiology Neuropathology and Pathogenesis Alzheimers disease is the most common form of dementia and the most common neurodegenerative disease.
PATHOGENESIS OF ALZHEIMERS DISEASE. In the light of current literature we describe three different linkages between the present gut microbiome hypothesis and the other major theories for the pathogenesis of AD as follows. AD is a neurodegenerative disease and its pathogenesis has been attributed to extracellular aggregates of amyloid β Aβ plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles made of hyperphosphorylated τ-protein in cortical and limbic areas of the human brain. Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia. Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia. A the Aβ-amyloid hypothesis b the Aβ-amyloid oligomer hypothesis c the presenilin hypothesis d the Ca2dysregulation hypothesis e the lysosome hypothesis and f the tau hypothesis Fig. A number of hypotheses have been proposed that may explain AD pathogenesis. Alzheimers disease AD is one of the major causative factors to induce progressive dementia. Several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers disease AD possess significant vascular pathophysiology such as the disruption of BBB integrity and function Kapasi and Schneider 2016 Sagare et al 2012 Yarchoan et al 2012 Zlokovic 2011.
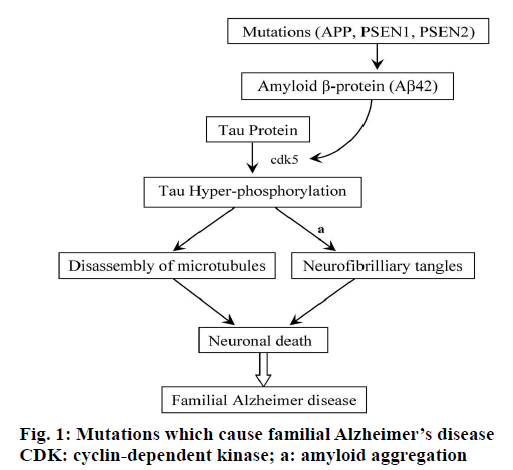
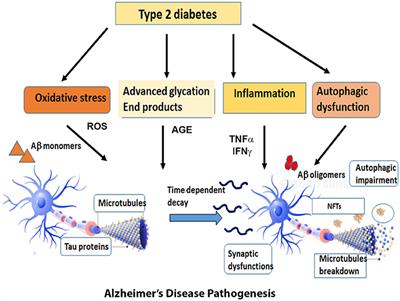
Type 2 diabetes mellitus T2DM and Alzheimers disease AD are both serious global health problems with high prevalence. Clinically it is characterized by loss of memory inability to learn new things loss of language function a deranged perception of space inability to do calculations indifference depression delusions and other manifestations. Mutations in PSEN1 are especially prominent in familial Alzheimers disease FAD where 221 mutations pathogenic mutations have been identified so far. In addition to deposits of amyloid β Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles growing evidence demonstrates that complex and multifaceted biological processes can arise during Alzheimer disease AD pathogenesis. Impaired gut microbiome flora inhibits the autophagy-mediated protein clearance process. A number of hypotheses have been proposed that may explain AD pathogenesis. In the light of current literature we describe three different linkages between the present gut microbiome hypothesis and the other major theories for the pathogenesis of AD as follows.































Post a Comment for "Pathogenesis Of Alzheimer's Disease"